Practical Questions
Question 1
A Prime-Adam integer is a positive integer (without leading zeros) which is a prime as well as an Adam number.
Prime number: A number which has only two factors, i.e. 1 and the number itself.
Example: 2, 3, 5, 7 ... etc.
Adam number: The square of a number and the square of its reverse are reverse to each other.
Example: If n = 13 and reverse of 'n' = 31, then,
(13)2 = 169
(31)2 = 961 which is reverse of 169
thus 13, is an Adam number.
Accept two positive integers m and n, where m is less than n as user input. Display all Prime-Adam integers that are in the range between m and n (both inclusive) and output them along with the frequency, in the format given below:
Test your program with the following data and some random data:
Example 1
INPUT:
m = 5
n = 100
OUTPUT:
THE PRIME-ADAM INTEGERS ARE:
11 13 31
FREQUENCY OF PRIME-ADAM INTEGERS IS: 3
Example 2
INPUT:
m = 100
n = 200
OUTPUT:
THE PRIME-ADAM INTEGERS ARE:
101 103 113
FREQUENCY OF PRIME-ADAM INTEGERS IS: 3
Example 3
INPUT:
m = 50
n = 70
OUTPUT:
THE PRIME-ADAM INTEGERS ARE:
NIL
FREQUENCY OF PRIME-ADAM INTEGERS IS: 0
Example 4
INPUT:
m = 700
n = 450
OUTPUT:
INVALID INPUT
Solution
import java.util.Scanner;
public class PrimeAdam
{
public static int reverse(int num) {
int rev = 0;
while (num != 0) {
int d = num % 10;
rev = rev * 10 + d;
num /= 10;
}
return rev;
}
public static boolean isAdam(int num) {
int sqNum = num * num;
int revNum = reverse(num);
int sqRevNum = revNum * revNum;
int rev = reverse(sqNum);
return rev == sqRevNum;
}
public static boolean isPrime(int num) {
int c = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= num; i++) {
if (num % i == 0) {
c++;
}
}
return c == 2;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter the value of m: ");
int m = in.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter the value of n: ");
int n = in.nextInt();
int count = 0;
if (m >= n) {
System.out.println("INVALID INPUT");
return;
}
System.out.println("THE PRIME-ADAM INTEGERS ARE:");
for (int i = m; i <= n; i++) {
boolean adam = isAdam(i);
if (adam) {
boolean prime = isPrime(i);
if (prime) {
System.out.print(i + " ");
count++;
}
}
}
if (count == 0) {
System.out.print("NIL");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("FREQUENCY OF PRIME-ADAM INTEGERS IS: " + count);
}
}Output





Question 2
Write a program to declare a matrix A[][] of order (M x N) where 'M' is the number of rows and 'N' is the number of columns such that the value of 'M' must be greater than 0 and less than 10 and the value of 'N' must be greater than 2 and less than 6. Allow the user to input digits (0 - 7) only at each location, such that each row represents an octal number.
Example:
| 2 | 3 | 1 | (decimal equivalent of 1st row = 153 i.e. 2x82 + 3x81 + 1x80) |
| 4 | 0 | 5 | (decimal equivalent of 2nd row = 261 i.e. 4x82 + 0x81 + 5x80) |
| 1 | 5 | 6 | (decimal equivalent of 3rd row = 110 i.e. 1x82 + 5x81 + 6x80) |
Perform the following tasks on the matrix:
- Display the original matrix.
- Calculate the decimal equivalent for each row and display as per the format given below.
Test your program for the following data and some random data:
Example 1:
INPUT:
M = 1
N = 3
ENTER ELEMENTS FOR ROW 1: 1 4 4
OUTPUT:
| FILLED MATRIX | DECIMAL EQUIVALENT | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4 | 4 | 100 |
Example 2:
INPUT:
M = 3
N = 4
ENTER ELEMENTS FOR ROW 1: 1 1 3 7
ENTER ELEMENTS FOR ROW 2: 2 1 0 6
ENTER ELEMENTS FOR ROW 3: 0 2 4 5
OUTPUT:
| FILLED MATRIX | DECIMAL EQUIVALENT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 3 | 7 | 607 |
| 2 | 1 | 0 | 6 | 1094 |
| 0 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 165 |
Example 3:
INPUT:
M = 3
N = 3
ENTER ELEMENTS FOR ROW 1: 2 4 8
OUTPUT:
INVALID INPUT
Example 4:
INPUT:
M = 4
N = 6
OUTPUT:
OUT OF RANGE
Solution
import java.util.Scanner;
public class OctalMatrix
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter the number of rows (M): ");
int m = in.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter the number of columns (N): ");
int n = in.nextInt();
if (m <= 0 || m >= 10 || n <= 2 || n >= 6) {
System.out.println("OUT OF RANGE");
return;
}
int a[][] = new int[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
System.out.println("ENTER ELEMENTS FOR ROW " + (i + 1) + ": ");
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
a[i][j] = in.nextInt();
if (a[i][j] < 0 || a[i][j] > 7) {
System.out.println("INVALID INPUT");
return;
}
}
}
System.out.println("FILLED MATRIX\tDECIMAL EQUIVALENT");
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int decNum = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
decNum += a[i][j] * Math.pow(8, n - j - 1 );
System.out.print(a[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.print("\t\t" + decNum);
System.out.println();
}
}
}Output




Question 3
Write a program to accept a sentence which may be terminated by either '.', '?' or '!' only. The words are to be separated by a single blank space and are in UPPER CASE.
Perform the following tasks:
- Check for the validity of the accepted sentence only for the terminating character.
- Arrange the words in ascending order of their length. If two or more words have the same length, then sort them alphabetically.
- Display the original sentence along with the converted sentence.
Test your program for the following data and some random data:
Example 1:
INPUT:
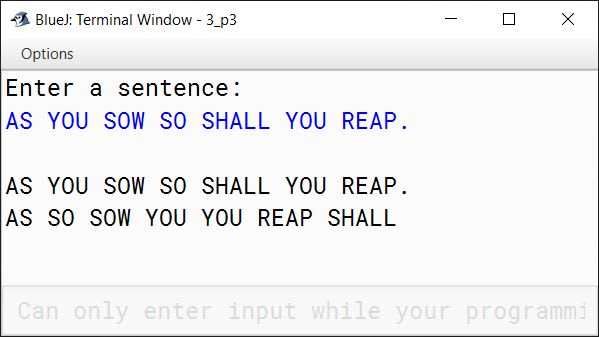
AS YOU SOW SO SHALL YOU REAP.
OUTPUT:
AS YOU SOW SO SHALL YOU REAP.
AS SO SOW YOU YOU REAP SHALL
Example 2:
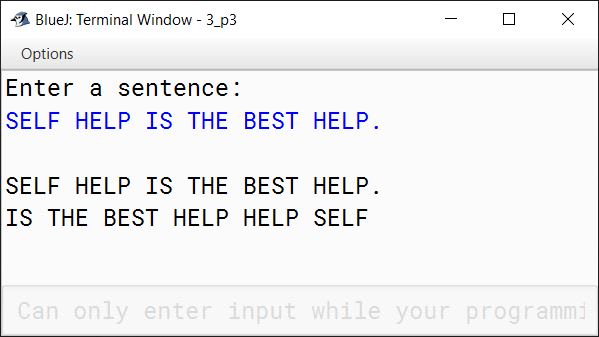
INPUT:
SELF HELP IS THE BEST HELP.
OUTPUT:
SELF HELP IS THE BEST HELP.
IS THE BEST HELP HELP SELF
Example 3:
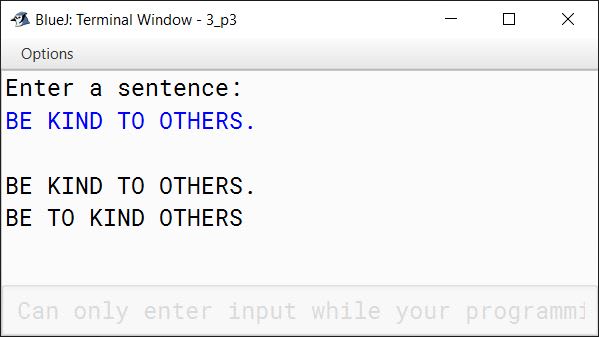
INPUT:
BE KIND TO OTHERS.
OUTPUT:
BE KIND TO OTHERS.
BE TO KIND OTHERS
Example 4:
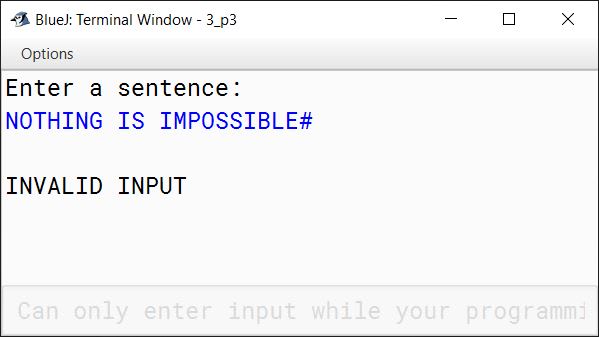
INPUT:
NOTHING IS IMPOSSIBLE#
OUTPUT:
INVALID INPUT
Solution
import java.util.*;
public class StringCheck
{
public static String sortString(String ipStr) {
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(ipStr);
int wordCount = st.countTokens();
String strArr[] = new String[wordCount];
for (int i = 0; i < wordCount; i++) {
strArr[i] = st.nextToken();
}
for (int i = 0; i < wordCount - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < wordCount - i - 1; j++) {
if (strArr[j].length() > strArr[j + 1].length()) {
String t = strArr[j];
strArr[j] = strArr[j+1];
strArr[j+1] = t;
}
if (strArr[j].length() == strArr[j + 1].length()
&&(strArr[j].compareTo(strArr[j+1]) > 0))
{
String t = strArr[j];
strArr[j] = strArr[j+1];
strArr[j+1] = t;
}
}
}
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
for (int i = 0; i < wordCount; i++) {
sb.append(strArr[i]);
sb.append(" ");
}
/*
* trim will remove the extra space added
* to the end of the string in the loop above
*/
return sb.toString().trim();
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a sentence:");
String str = in.nextLine();
int len = str.length();
System.out.println();
if (str.charAt(len - 1) != '.'
&& str.charAt(len - 1) != '?'
&& str.charAt(len - 1) != '!') {
System.out.println("INVALID INPUT");
return;
}
/*
* str.substring(0, len - 1) removes the
* '.', '?', '!' at the end of the string
*/
String sortedStr = sortString(str.substring(0, len - 1));
System.out.println(str);
System.out.println(sortedStr);
}
}Output