Section A (Very Short Answer Questions 2 Marks Each)
Question 1
(a) Write the molecular formula of the following carbon compounds :
- Methane
- Propane
(b) Carbon compounds have low melting and boiling points. Why ?
Answer
(a) Molecular formula of the carbon compounds are:
- Methane — CH4
- Propane — C3H8
(b) As carbon compounds are covalent compounds and forces of attraction between these molecules is not very strong hence they have low melting and boiling points.
Question 2
The electrons in the atoms of two elements X and Y are distributed in three shells having 1 and 7 electrons respectively in their outermost shells.
(a) Write the group numbers of these elements in the Modern Periodic Table.
(b) Write the molecular formula of the compound formed when X and Y combine with each other.
(c) Which of the two is electropositive ?
Answer
(a) As the number of electrons present in the outermost shell determines the group number of any element, hence, element X belongs to group 1 (as it has one electron in the outermost shell), and element Y belongs to group 17 (as it has seven electrons in the outermost shell.)
(b) Molecular formula of the compound formed between X and Y is XY.
Reason — As element Y has 7 electrons in its outermost shell, it only needs 1 electron to complete its octet and element X has 1 electron in its outer shell, it will try to donate it and attain a stable octet (because it has 8 electrons in 2nd shell). As a result, element Y will take one of the electrons released by element X and both will attain a stable configuration. Hence, the resulting molecule will have the molecular formula XY.
(c) As X donates its electrons hence, it is said to be electropositive.
Question 3
(a) Which of the following flowers will have higher possibility of self-pollination ?
Mustard, Papaya, Watermelon, Hibiscus
(b) List the two reproductive parts of a bisexual flower.
Answer
(a) Mustard and Hibiscus will have higher possibility of self-pollination as they are bisexual flowers. Papaya and Watermelon have unisexual flower and hence they are cross pollinated.
(b) The two reproductive parts of a bisexual flower are:
- Androecium (male part)
- Gynoecium (female part)
Question 4
Which one of the two multicellular organisms Spirogyra and Planaria reproduces by regeneration and why? Give an example of any other organism which can also reproduce by the same process.
Answer
Planaria reproduces by regeneration. It is because they have specialised cells. These cells proliferate and make large numbers of cells. From this mass of cells, different cells undergo changes to become various cell types and tissues. Thus, different parts develop to make complete organisms.
Hydra is other organism which can also reproduce by the same process.
Question 5(a)
What is variation ? List two main reasons that may lead to variation in a population.
Answer
The small differences among the individuals of the same species are called variations. Variation are very important in population as they ensure the survival of the species.
Two main reasons that may lead to variation in a population are:
- The DNA copying mechanism is not absolutely accurate, and the resultant errors are a source of variations in populations of organisms.
- The sexual mode of reproduction incorporates a process of combining DNA from two different individuals during reproduction which creates variation.
Question 5(b)
(i) In a cross between violet flowered plants and white flowered plants, state the characteristics of the plants obtained in the F1 progeny.
(ii) If the plants of F1 progeny are self-pollinated, then what would be observed in the plants of F2 progeny ?
(iii) If 100 plants are produced in F2 progeny, then how many plants will show the recessive trait ?
Answer
(i) In a cross between violet flowered (VV) plants and white flowered (vv) plants, the plants obtained in the F1 progeny will bear purple flowers as purple flower is dominant trait. Genotype of the F1 progeny will be heterozygous (Vv).
(ii) If the plants of F1 progeny are self-pollinated, the plants in F2 generation will be purple flowered and white flowered in a ratio of 3:1
(iii) If 100 plants are produced in F2 progeny, then 25 plants will show the recessive trait.
Question 6(a)
(i) Name and state the rule to determine the direction of force experienced by a current carrying straight conductor placed in a uniform magnetic field which is perpendicular to it.
(ii) An alpha particle while passing through a magnetic field gets projected towards north. In which direction will an electron project when it passes through the same magnetic field ?
Answer
(i) Fleming's left hand rule.
According to this rule : Stretch the thumb, fore finger and middle finger of your left hand such that they are mutually perpendicular. If the forefinger points in the direction of magnetic field and the middle finger in the direction of current, then the thumb will point in the direction of motion or force acting on conductor.
(ii) As the direction of the force on a negatively charged electron will be opposite to that of a positively charged alpha particle hence, an electron will experience a force that pushes it towards the south when it passes through the same magnetic field as that of alpha particle.
Question 6(b)
(i) What is a solenoid ?
(ii) Draw the pattern of magnetic field lines of the magnetic field produced by a solenoid through which a steady current flows.
Answer
(i) A coil of many circular turns of insulated copper wire wrapped closely in the shape of a cylinder is called a solenoid.
(ii) The pattern of magnetic field lines of the magnetic field produced by a solenoid through which a steady current flows is shown below:

Question 7(a)
What is ozone ? How is it formed in the upper layers of the Earth's atmosphere ? How does ozone affect our ecosystem ?
Answer
Ozone is a gas which is formed when an oxygen molecule (O2) combines with another oxygen atom (O). Thus, Ozone (O3) is a molecule formed by three atoms of oxygen.
At the higher levels of the atmosphere, UV radiation acts on oxygen (O2) molecule. The higher energy UV radiations split apart some molecular oxygen (O2) into free oxygen (O) atoms. These atoms then combine with the molecular oxygen to form ozone.
O2 O + O
O2 + O ⟶ O3
Ozone is present at the higher levels of the atmosphere and it shields the surface of the earth from ultraviolet (UV) radiation of the Sun. Therefore, it helps to protect all ecosystems/organisms from highly damaging radiations that can cause problems like skin cancer and cataract in humans and potential damage to some marine organisms and plants. Ozone also helps to maintain the temperature of earth.
Question 7(b)
(i) List two human-made ecosystems.
(ii) "We do not clean a pond in the same manner as we do in an aquarium." Give reason to justify your answer.
Answer
(i) Two human-made ecosystems are:
- Agricultural field
- Aquarium
(ii) Pond has a natural ecosystem. It has many decomposers present in it due to which the pond is naturally cleaned up. It is a balanced and self sustaining ecosystem. An aquarium, however is not self sustaining. We need to clean it up and change its water in order to remove the waste produced by the fishes or the leftover food in there as these may further act as toxins for water and aquatic life.
Section B (Short Answer Questions 3 Marks Each)
Question 8
(a) List two advantages of adopting the atomic number of an element as the basis of classification of elements in the Modern Periodic Table.
(b) Write the electronic configurations of the elements X (atomic number 13) and Y (atomic number 20).
Answer
(a) The advantages of adopting the atomic number of an element as the basis of classification of elements in the Modern Periodic Table are :
Elements in the same group have same number of valence electrons. It correlates the position of the element with its electronic configuration clearly.
The completion of each period is more logical. Across a period as the atomic number increases the energy shells are gradually filled up until an inert gas configuration is reached.
(b) Electronic configuration of X(13) = 2, 8, 3 and Y(20) = 2, 8, 8, 2
Question 9(a)
Draw two different possible structures of a saturated hydrocarbon having four carbon atoms in its molecule. What are these two structures of the hydrocarbon having same molecular formula called ? Write the molecular formula and the common name of this compound. Also write the molecular formula of its alkyne.
Answer
(a) Two different possible structures of a saturated hydrocarbon having four carbon atoms in its molecule are shown below:
1. n-butane

2. Isobutane

These structures having same molecular formula and different structural formula are called isomers.
Molecular formula — C4H10
Common Name — Butane
Molecular formula of its alkyne — C4H6 [Butyne]
Question 9(b)
(i) Write the molecular formula of benzene and draw its structure.
(ii) Write the number of single and double covalent bonds present in a molecule of benzene.
(iii) Which compounds are called alkynes ?
Answer
(i) Molecular formula of benzene — C6H6
Structure of benzene:

(ii) In the structure formula of benzene there are 3 double bonds and 9 single bonds present.
(iii) Organic compounds of carbon and hydrogen containing one or more triple bonds are called alkynes. Their general formula is CnH2n-2.
Question 10
(a) Mention one function each of the following organs in human male reproductive system :
- Testis
- Scrotum
- Vas deferens
- Prostate gland
(b) Name the type of germ cell which
- is motile
- stores food.
Answer
(a) Functions of given organs in human male reproductive system:
- Testis — It produces and stores sperms (male gamete).
- Scrotum — It holds the testis outside the body and maintains the temperature of testes at 2 to 3°C less than body temperature for the maturation of sperms.
- Vas deferens — Transports the sperm from epididymis to ejaculatory duct.
- Prostate gland — It pours an alkaline secretion into the semen as it passes through the urethra. It neutralises acid in female's vagina.
(b) Type of germ cell which:
- is motile — Sperm
- stores food — Ovum
Question 11
(a) Three resistors R1, R2 and R3 are connected in parallel and the combination is connected to a battery, an ammeter, a voltmeter and a key. Draw suitable circuit diagram to show the arrangement of these circuit components along with the direction of current flowing.
(b) Calculate the equivalent resistance of the following network :

Answer
(a) Circuit diagram showing the arrangement:

(b) We can see from figure that resistances R2 and R3 each of 10 Ω are connected in parallel. So, the equivalent resistance Rp is:
Now, R1, Rp and R4 (each of 5 Ω ) are connected in series
∴ Requi = 5 + 5 + 5 = 15 Ω
So, equivalent resistance of the circuit = 15 Ω.
Question 12(a)
(i) Define Electric Power and write its SI unit.
(ii) Two bulbs rated 100 W; 220 V and 60 W; 220 V are connected in parallel to an electric mains of 220 V. Find the current drawn by the bulbs from the mains.
Answer
(i) Electric power is the rate at which electric energy is dissipated or consumed in an electric circuit.
The SI unit of electric power is watt (W).
(ii) Given,
Voltage across the circuit = 220 V
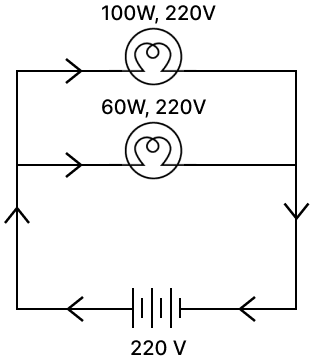
Power of first bulb (B1) be (P1) = 100 W
Power of second bulb (B2) be P2 = 60 W
P =
or
R =
Resistance across B1 :
Substituting in formula we get,
R1 = = 484 Ω
I =
Substituting in formula we get,
I1 = = 0.454 A
Resistance across B2 :
Substituting in formula above we get,
R2 = = 806.6 Ω
and
I2 = = 0.272 A
Now as they are connected in parallel, so the equivalent resistance is given by,
So, equivalent resistance = 302.5 Ω
And current through mains is
I = = 0.727 A
Hence, current drawn by the bulbs from the mains = 0.727 A
Question 12(b)
(i) State Joule's law of heating. Express it mathematically when an appliance of resistance R is connected to a source of voltage V and the current I flows through the appliance for a time t.
(ii) A 5 Ω resistor is connected across a battery of 6 volts. Calculate the energy that dissipates as heat in 10 s.
Answer
(i) Joules law of heating states that the heat dissipated across a resistor is directly proportional to
- the square of the current flowing through it
- resistance of the conductor
- duration of flow of current
i.e., H = I2Rt
(ii) Given,
Resistance (R) = 5 Ω
Voltage (V) = 6 V
Time (t) = 10 s
From ohm's law :
V = IR
6 = I x 5
I = = 1.2 A
Energy dissipated (H) = I2Rt
Substituting we get,
H = 1.2 x 1.2 x 5 x 10 = 72 J
Hence, energy dissipated = 72 J.
Question 13
(a) Name the group of organisms which form in the first trophic level of all food chains. Why are they called so ?
(b) Why are the human beings most adversely affected by bio-magnification ?
(c) State one ill-effect of the absence of decomposers from a natural ecosystem.
Answer
(a) The group of organisms which form the first trophic level of all food chains are producers. They are called so because they are the only one to change the light energy of sun to chemical energy of food. The same energy goes to other trophic levels in food chains
(b) Bio-magnification refers to progressive accumulation of chemicals at each trophic level. Human beings are most adversely affected by bio-magnification because they are at the top of any food chain. Therefore, the maximum concentration of these chemicals get accumulated in human bodies.
(c) Without decomposers, the organic matter would not be efficiently broken down and recycled into essential nutrients, leading to the accumulation of dead organic matter in the ecosystem. This will disrupt the natural recycling of nutrients, negatively impacting soil fertility, promoting disease, and hindering the overall health and functioning of the ecosystem.
Section C (Source/Case Based Questions 4 Marks Each)
Question 14
The mechanism by which the sex of an individual is determined is called sex-determination. In human beings, sex of a newborn is genetically determined, whereas in some others it is not. There are 46 (23 pairs) chromosomes in human beings. Out of these, 44 (22 pairs) control the body characters and 2 (one pair) are known as sex chromosomes. The sex chromosomes are of two types X chromosome and Y chromosome. At the time of fertilisation, depending upon which type of male gamete fuses with the female gamete, the sex of the newborn child is decided.
(a) Why is a pair of sex chromosomes in human beings called a mismatched pair in terms of type and size ?
(b) Out of male or female, which of them has a perfect pair of sex chromosomes ? In case of a perfect pair, will the gametes produced be of the same kind or of a different kind ?
(c) (i) Name two animals whose sex is not genetically determined. Explain the process of their sex determination.
OR
(ii) With the help of a flowchart only, show how sex is genetically determined in human beings.
Answer
(a) A pair of sex chromosomes in human beings is called a mismatched pair in terms of type and size because in males one chromosome is a normal-sized X while the other is a short one called Y. Such a pair of chromosome is known as heteromorphic.
(b) Female has a perfect pair of sex chromosomes. Since all chromosomes are alike, the gametes produced are of same kind.
(c) (i) The two animals whose sex is not genetically determined are Snail and Green Sea Turtle.
- Green Sea Turtle — Green Sea Turtle exhibits temperature-dependent sex determination. Temperature at which the eggs are incubated determines the sex of the offsprings. Cooler temperatures (around 29°C) result in the development of male hatchlings, while warmer temperatures (around 33°C) lead to the development of female hatchlings.
- Snail — In snails, individuals can change sex, indicating that sex is not genetically determined. The snail is born as a male but eventually changes into a female. Snails use physical contact with other snails to guide sex change.
OR
Below flowchart shows genetic sex determination in human beings:

Question 15
A student fixes a sheet of white paper on a drawing board using some adhesive materials. She places a bar magnet in the centre of it and sprinkles some iron filings uniformly around the bar magnet using a salt-sprinkler. On tapping the board gently, she observes that the iron filings have arranged themselves in a particular pattern.
(a) Draw a diagram to show this pattern of iron filings.
(b) Draw the magnetic field lines of a bar magnet showing the poles of the bar magnet as well as the direction of the magnetic field lines.
(c) (i) How is the direction of magnetic field at a point determined using the field lines ? Why do two magnetic field lines not cross each other ?
OR
(ii) How are the magnetic field lines of a bar magnet drawn using a small compass needle ? Draw one magnetic field line each on both sides of the magnet.
Answer
(a) Below diagram shows the pattern of iron filings:

(b) The magnetic field lines of a bar magnet and its poles are shown below:

(c) (i) The direction of the magnetic field lines at a place can be determined by using a compass needle.
Two magnetic field lines never intersect each other. If they would intersect, this would mean that there are two directions of the field at the specific point which is not possible.
OR
(ii) Magnetic field lines can be mapped out using a small compass.
We will mark the position of two ends of the needle of the compass.
Now we will move the needle to a new position such that its south pole occupies the position previously occupied by its north pole.
In this way, we will proceed step by step till we reach the south pole of the magnet as shown in Fig.
Now we will join the points marked on the paper by a smooth curve. This curve represents a field line.
We will repeat the above procedure, and get the magnetic field lines around the magnet.
